Heat Equity Design Toolkit - Street-Tree Canopy for Pedestrian Comfort
Shaiba Bano Siddiqui
Independent Study - MS Urban Design (Fall 2025), Georgia Institute of Technology
Author: Shaiba Bano Siddiqui
Advisor: Patrick Kastner
Secondary Advisor: Rounaq Basu
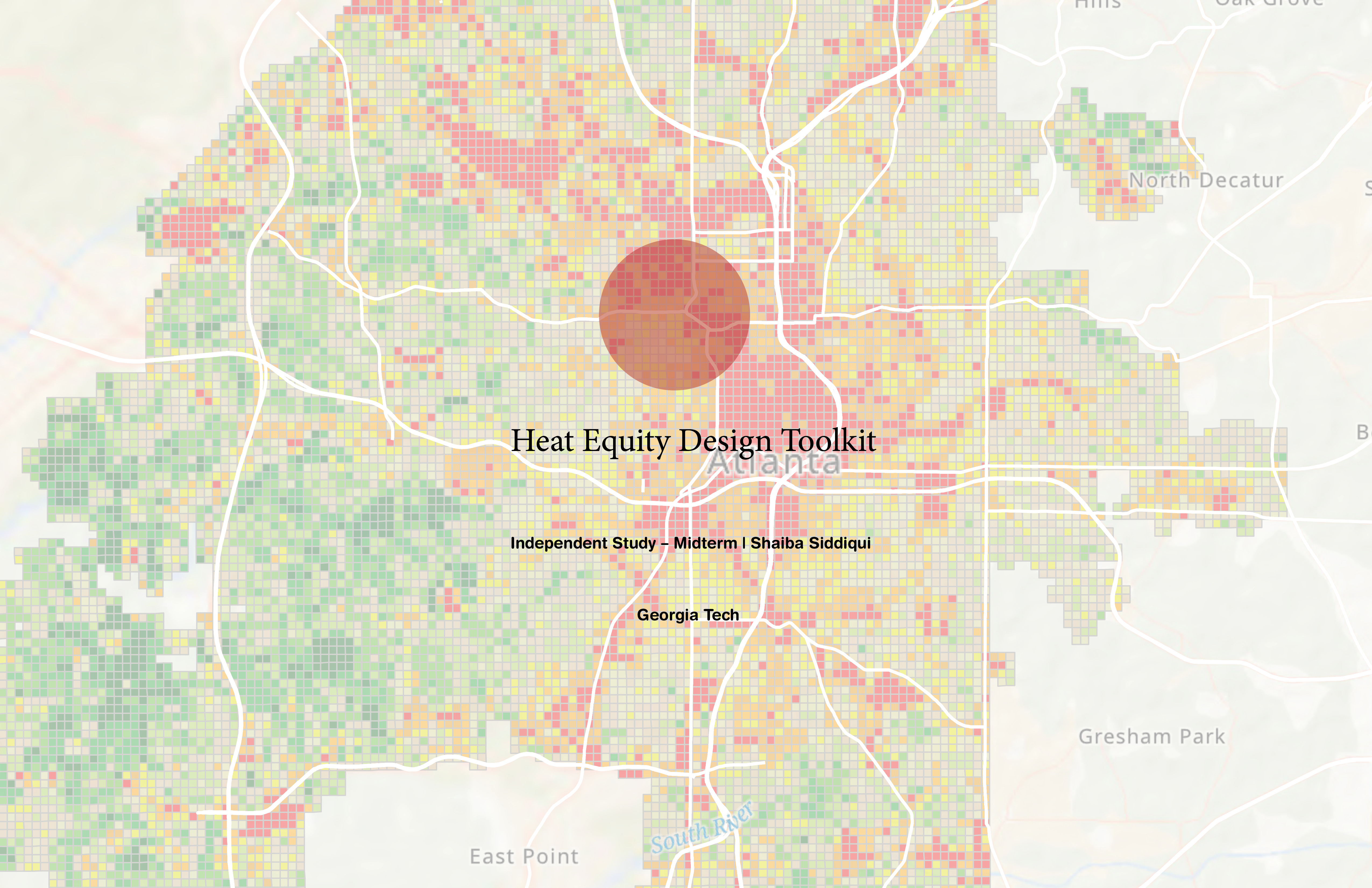
Overview
Urban heat exposure disproportionately impacts low-income and transit-dependent neighborhoods, where limited tree canopy, wide asphalt corridors, and fragmented shade create unsafe pedestrian conditions. While trees are widely recognized as a cooling strategy, how trees are spatially configured along streets (spacing, side placement, clustering) strongly influences pedestrian-scale thermal comfort.
This study investigates how street-tree canopy configuration can reduce Mean Radiant Temperature (MRT) and heat exposure for pedestrians and transit users in heat-vulnerable neighborhoods across Atlanta, with a corridor-scale simulation focus on Joseph E. Boone Boulevard (Vine City / English Avenue).
📄 Final Report (PDF): https://github.com/sshaiba3/MSUD_Independent_Study_2025/blob/main/Shaiba%20Siddiqui-Independent%20Study.pdf
Research Question
How does the spatial configuration of street-tree canopy (spacing, side placement, clustering) reduce heat exposure for pedestrians and transit users in low-income neighborhoods across Atlanta?
Study Area
-
City: Atlanta, Georgia
-
Neighborhood Focus: English Avenue / Vine City (Westside Atlanta)
-
Corridor Focus: Joseph E. Boone Boulevard
-
Context: low canopy, high heat intensity, transit-dependent population, and higher displacement / green gentrification risk
Methodology
1) Citywide Spatial Analysis (GIS)
Datasets
-
Urban Tree Canopy (UTC, 2018)
-
Urban Heat Intensity Raster (City of Atlanta)
-
Median Household Income (ACS 2022)
-
Transit routes + stops
Steps
-
Standardized projections + city boundary
-
Zonal statistics (heat + canopy by census tract)
-
Joined socioeconomic data to environmental layers
-
Composite overlays to identify low-canopy + high-heat + low-income priority zones
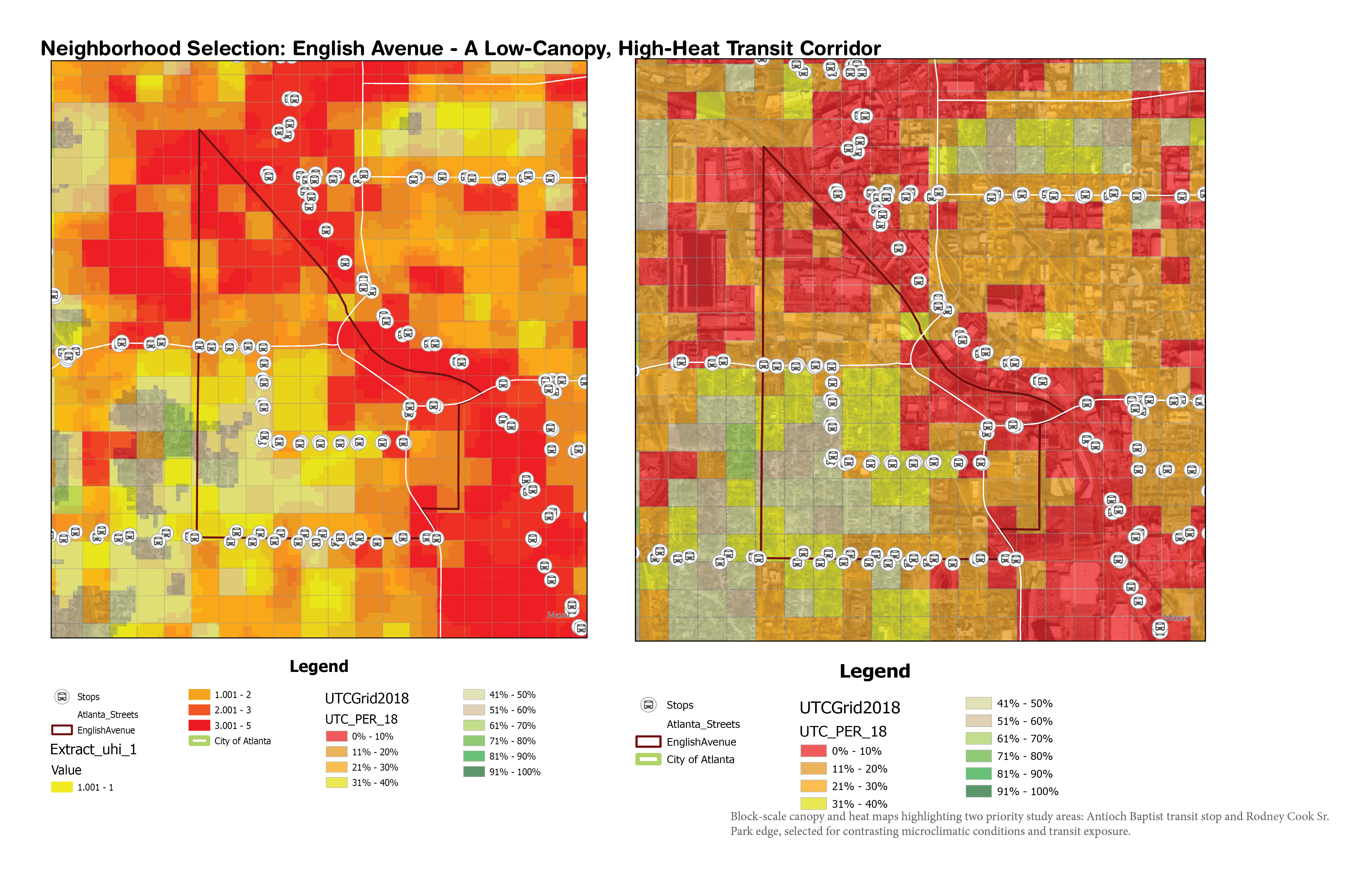
2) Corridor & Block Selection
Joseph E. Boone Blvd was selected due to:
-
Wide right-of-way (~150 ft)
-
Sparse and fragmented canopy
-
High pedestrian and bus-stop exposure
-
Proximity to community assets and BeltLine development pressure
3) Microclimate Simulation
Tool: Eddy3D Outdoor+ (Rhino + Grasshopper)
Simulated outputs: MRT, air temperature, surface temperature, solar exposure, wind flow
Simulation periods (Peak Summer):
-
Morning: 7–9 AM
-
Afternoon (Peak Heat): 2–4 PM
-
Evening: 6–8 PM
-
Days 172–174 (June 21–23)

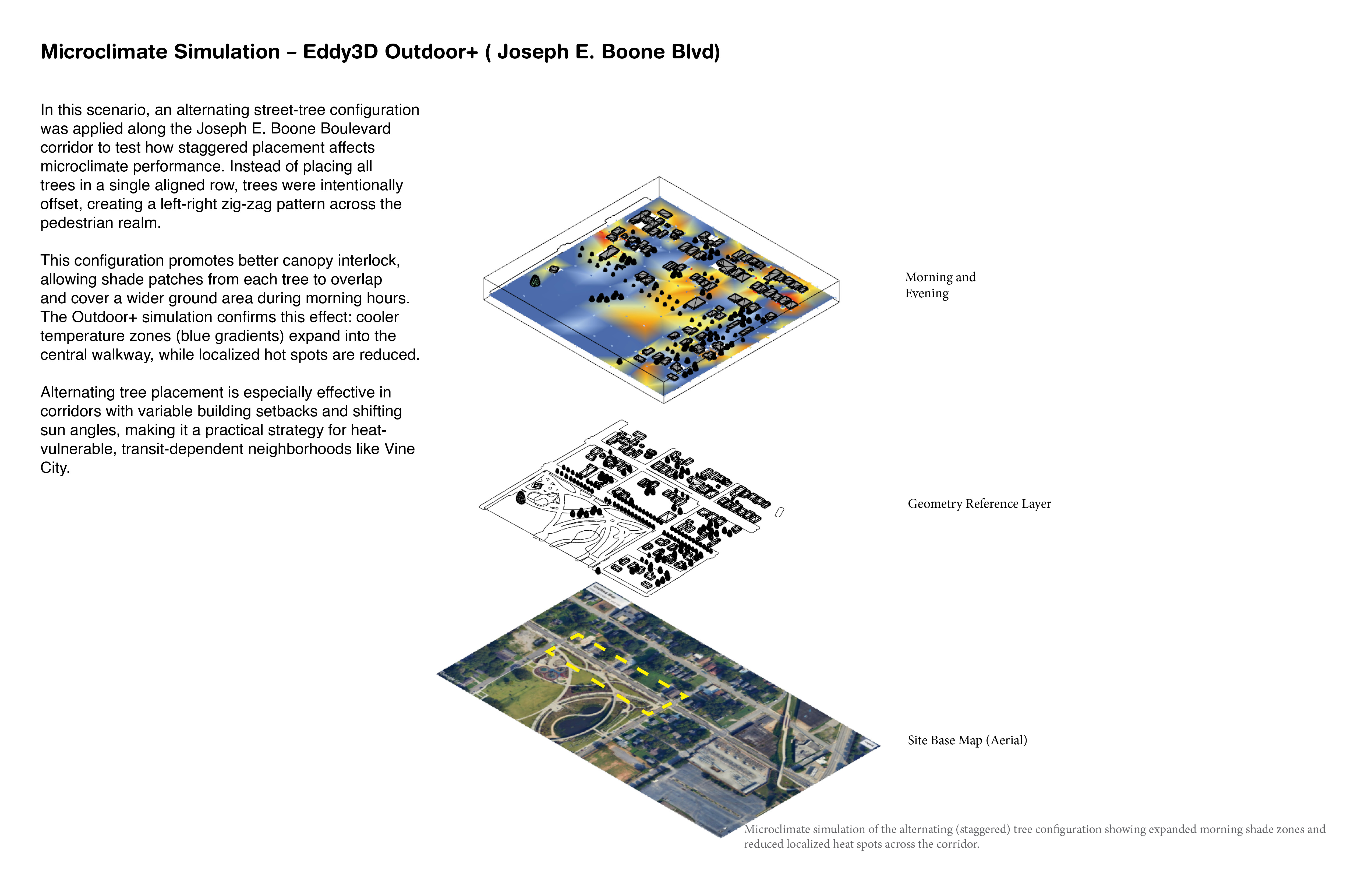
Tree Configuration Scenarios Tested
-
Existing Conditions
Sparse, inconsistent canopy; long unshaded sidewalk segments
-
Uniform Dual-Sided Canopy
Trees on both sides; ~20 ft (6–7 m) spacing; continuous shade rhythm
-
Alternating (Staggered) Placement
Offset left–right; reduced canopy overlap
-
Clustered Planting at Nodes
Increased density at bus stops, intersections, and crossings
Key Findings
-
Uniform dual-sided spacing performs best for wide corridors like Joseph E. Boone Blvd
-
Continuous canopy significantly reduces MRT along sidewalks and transit stops
-
Alternating spacing creates patchy cooling (more suitable for narrower streets)
-
Clustering at nodes improves localized comfort, but works best when paired with corridor continuity
-
Benefits are strongest during afternoon peak-heat hours
Equity & Gentrification Lens
Cooling infrastructure can increase development pressure if implemented without safeguards. This study integrates:
-
Heat vulnerability mapping
-
Income + race overlays
-
Green gentrification literature
Key takeaway: equitable cooling must be paired with community stewardship, policy safeguards, and anti-displacement strategies so benefits remain with existing residents.
Toolkit Outputs
This work culminates in a Heat Equity Design Toolkit that translates climate data + microclimate simulation into actionable street-design guidance:
-
Corridor-specific canopy spacing guidelines
-
Tree placement typologies by street width
-
Transit-stop shading strategies
-
Native tree species recommendations (Atlanta)
-
Equity-first implementation principles
Recommended Native / Local Street Trees (Atlanta)
-
Willow Oak (Quercus phellos)
-
Southern Red Oak (Quercus falcata)
-
American Elm (Dutch-Elm–resistant cultivars)
-
Sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua)
-
Blackgum / Tupelo (Nyssa sylvatica)
-
Eastern Redbud (Cercis canadensis) — understory
-
Loblolly Pine (Pinus taeda) — wind and winter buffering
References (APA)
Rodriguez, F., Santana, J., & Krüger, E. (2025). Local impacts of street trees on outdoor thermal comfort in street canyons. Urban Climate, 49, 101528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2023.101528
City of Atlanta. (2015). Atlanta Climate Action Plan. https://www.atlantaga.gov
City of Atlanta & Trees Atlanta. (2018). Urban Tree Canopy Assessment. https://www.treesatlanta.org
Environmental Protection Agency. (2023). Heat island effect and mitigation strategies. https://www.epa.gov/heatislands
Hoffman, J. S., Shandas, V., & Pendleton, N. (2020). The effects of historical housing policies on resident exposure to intra-urban heat. Climate, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010012
Gould, K., & Lewis, T. (2017). Green gentrification. Routledge.
Tools & Software
-
ArcGIS Pro
-
Rhino + Grasshopper
-
Eddy3D Outdoor+
-
Google Earth (basemap reference)
-
Adobe Illustrator / InDesign (graphics)
Limitations & Future Work
This study simulates a limited number of representative street segments and should be interpreted as comparative performance rather than absolute temperature prediction. Future work can:
-
Test additional corridors and street orientations
-
Expand seasonal/diurnal variation testing
-
Integrate housing + displacement indicators more directly
-
Combine canopy strategies with cool pavements, shade structures, and transit shelter retrofits
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Patrick Kastner and Rounaq Basu for guidance, and to Georgia Tech’s urban climate research community for the intellectual and technical foundation for this work.
Source
Link to the repository.